Targeting rules determine when specific token templates are applied. You can create conditional logic based on user attributes, token types, and other criteria to ensure the right template is used for each authentication scenario.
Targeting rules allow you to:
- Apply templates conditionally: Use different templates for different users, applications, or contexts
- Segment token behavior: Provide different token structures for various use cases
- Maintain flexibility: Change token behavior without code modifications
- Support multi-tenancy: Apply different templates per tenant or user group
- Navigate to [ENVIRONMENT] → Security → Token management
- Click on the Targeting tab
- Click Add Rule to create a new targeting rule
Prerequisites
Prerequisites
The Add Rule button becomes available only after you have created at least one JWT template. Create your first template in the Token templates tab before setting up targeting rules.
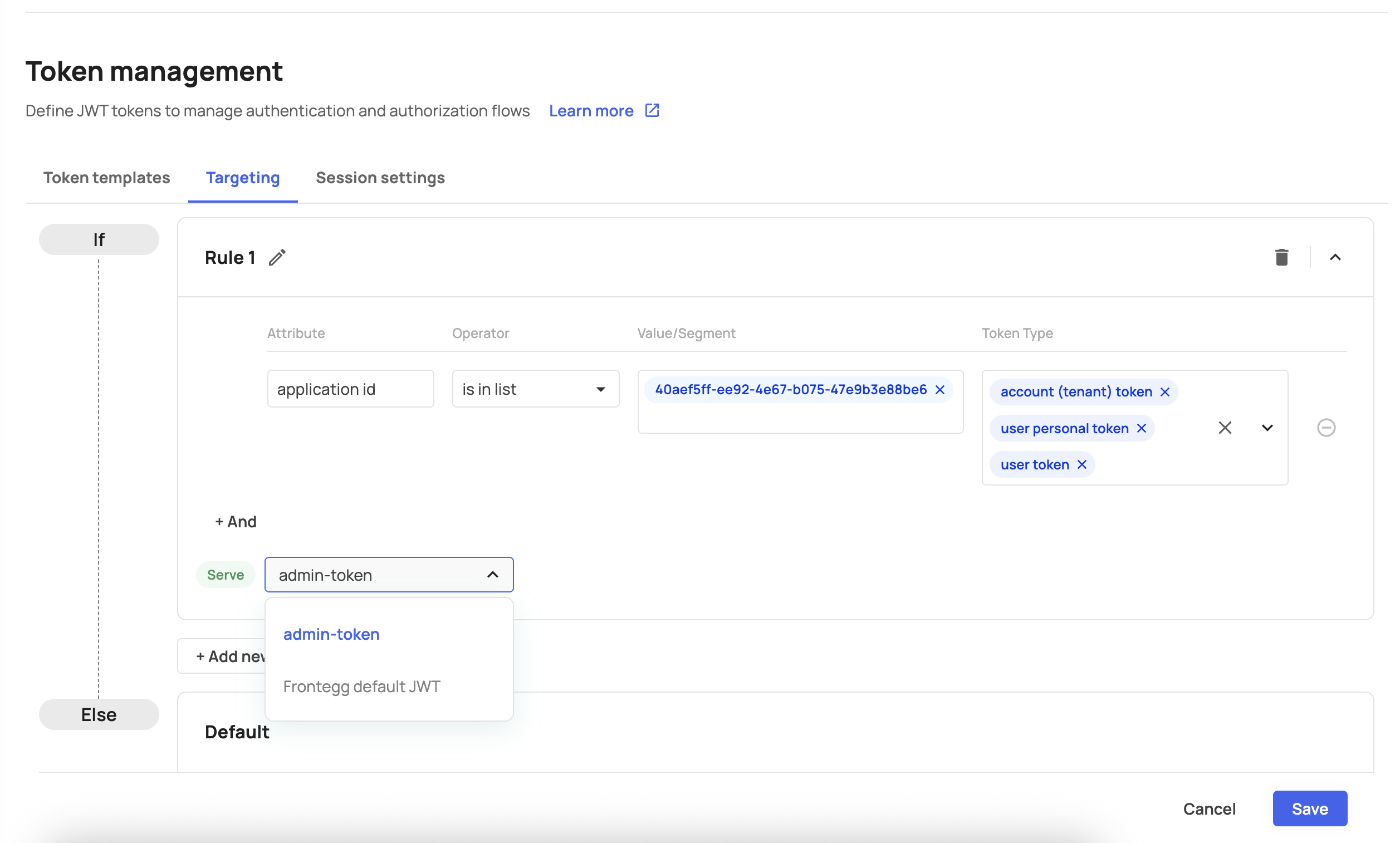
Each targeting rule consists of:
- Attributes: The user or context property to evaluate
- Operators: How to compare the attribute value
- Values: The target values to match against
- Token types: Which token types this rule applies to
Targeting rules can be based on the following attributes (listed in order of appearance):
| Attribute | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| User ID | Unique user identifier | "e3b0c442-98fc-4c39-b9e3-8d9f3e1e5a2f", "7f8c3b1a-4d5e-6f7a-8b9c-0d1e2f3a4b5c" |
| User email | User's email address | "john@company.com", "admin@domain.org" |
| Attribute | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Application ID | Frontegg application identifier | "a1b2c3d4-5e6f-7a8b-9c0d-1e2f3a4b5c6d", "f9e8d7c6-b5a4-3210-9876-543210fedcba" |
| Attribute | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Tenant ID | Account/tenant identifier | "9b8a7c6d-5e4f-3a2b-1c0d-e9f8a7b6c5d4", "1a2b3c4d-5e6f-7a8b-9c0d-1e2f3a4b5c6d" |
| Attribute | Description | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Role ID | User's assigned role identifier | "2c3d4e5f-6a7b-8c9d-0e1f-2a3b4c5d6e7f", "8f7e6d5c-4b3a-2109-8765-fedcba098765" |
Choose from the following operators to define your matching logic (listed in order of appearance):
| Operator | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Is in list | Value exists in provided list | Multiple allowed values |
| Is not in list | Value does not exist in list | Multiple excluded values |
| Operator | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Contains | Value contains substring | Partial matching |
| Does not contain | Value does not contain substring | Exclude patterns |
| Ends with | Value ends with substring | Domain or suffix matching |
| Does not end with | Value does not end with substring | Exclude specific endings |
Select which token types the targeting rule applies to. All three types are selected by default when the dropdown opens:
| Token Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| User token | Standard user authentication tokens | Regular user login sessions |
| User personal token | Personal API tokens for users | User-generated API keys |
| Account (tenant) token | Tenant-level authentication tokens | Organization-wide API access |
- Default behavior: All token types are selected when creating a new rule
- Selective application: Uncheck token types to exclude them from the rule
- Multiple rules: Create separate rules for different token type combinations
Rule configuration:
- Attribute: Role ID
- Operator: Is in list
- Value:
2c3d4e5f-6a7b-8c9d-0e1f-2a3b4c5d6e7f - Token types: User token, User personal token
Result: Admin users receive tokens with extended claims and longer expiration times.
Rule configuration:
- Attribute: Application ID
- Operator: Is in list
- Value:
a1b2c3d4-5e6f-7a8b-9c0d-1e2f3a4b5c6d - Token types: User token
Result: Mobile application users receive lightweight tokens with minimal claims for better performance.
Rule configuration:
- Attribute: Tenant ID
- Operator: Is in list
- Value:
9b8a7c6d-5e4f-3a2b-1c0d-e9f8a7b6c5d4 - Token types: All types
Result: Users from the enterprise tenant receive tokens with additional custom claims.
Rule configuration:
- Attribute: User email
- Operator: Does not end with
- Value:
@yourcompany.com - Token types: User token, User personal token
Result: External users (not from your company domain) receive tokens with restricted claims.
Rule configuration:
- Attribute: Role ID
- Operator: Is in list
- Values:
3d4e5f6a-7b8c-9d0e-1f2a-3b4c5d6e7f8a,4e5f6a7b-8c9d-0e1f-2a3b-4c5d6e7f8a9b,5f6a7b8c-9d0e-1f2a-3b4c-5d6e7f8a9b0c - Token types: Account (tenant) token
Result: Service accounts and API users receive specialized tokens for machine-to-machine communication.
- First match wins: Rules are evaluated in the order they appear
- Default fallback: If no rules match, the default template is used
- Rule ordering: Arrange rules from most specific to most general
You can create multiple targeting rules for the same template:
- Specific conditions first: Place more specific rules at the top
- Broad conditions last: Use general rules as fallbacks
- Non-overlapping logic: Ensure rules don't conflict with each other
Before deploying targeting rules:
- Review logic: Ensure your conditions match intended users
- Test scenarios: Verify rules work with sample data
- Monitor results: Check that the correct templates are being applied
- Keep it simple: Start with basic rules and add complexity as needed
- Document logic: Clearly document why each rule exists
- Regular review: Periodically review and update targeting rules
- Minimize rules: Fewer rules mean faster evaluation
- Efficient operators: Use list matching for specific values or string matching for patterns
- Attribute selection: Choose attributes that are readily available
- Principle of least privilege: Ensure rules don't accidentally grant excessive access
- Sensitive data: Be careful with rules that might expose sensitive information
- Audit trail: Keep track of rule changes and their impact
Rule not applying:
- Check rule order (first match wins)
- Verify attribute values match exactly
- Ensure token type is selected
Unexpected template usage:
- Review rule evaluation order
- Check for overlapping conditions
- Verify fallback behavior
Performance issues:
- Reduce number of rules
- Optimize operator selection
- Consider caching strategies
- Test with known values: Use specific user IDs or emails for testing
- Check logs: Monitor authentication logs for rule evaluation
- Gradual rollout: Test rules with small user groups first
Rule evaluation order
Rule evaluation order
Targeting rules are evaluated in the order they appear. The first matching rule determines which template is used. Arrange rules from most specific to most general.
Default fallback
Default fallback
If no targeting rules match, or if the matched template is unavailable, Frontegg will fall back to the default JWT structure to ensure authentication continues to work.